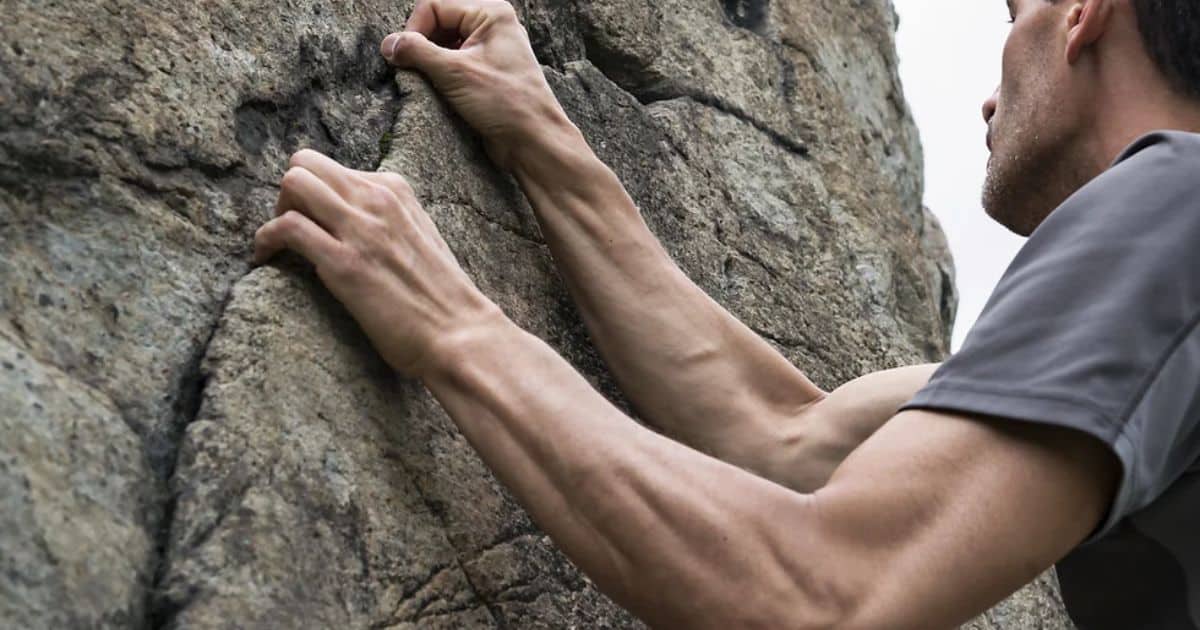
In the world of climbing, strength and endurance are paramount. Climbers not only challenge gravity but also their own physical limits. To conquer the heights, climbers engage a variety of muscles throughout their bodies. From the intricate finger and hand muscles that provide grip, to the powerful leg muscles that propel them upwards, each muscle group plays a crucial role in this demanding sport. Understanding the specific muscles worked in climbing can help climbers tailor their training and reach new heights of performance.
Key Takeaways
- Finger and hand muscles, specifically the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum superficialis, are crucial for gripping and holding onto rock surfaces.
- Forearm muscles play a vital role in maintaining grip strength in climbing, and repetitive gripping and pulling motions help develop and strengthen these muscles.
- Grip strength training increases finger flexor strength and improves forearm endurance, leading to enhanced overall climbing performance.
- Core muscles, such as the rectus abdominis, obliques, erector spinae, and hip flexors, provide stability, balance, and power in climbing, and strengthening them is important for maintaining proper body alignment and control during climbing.
Finger and Hand Muscles
Climbers heavily engage the intricate network of finger and hand muscles to execute precise and controlled movements during their ascent. These muscles, including the flexor digitorum profundus and the flexor digitorum superficialis, play a crucial role in gripping and holding onto rock surfaces. As climbers progress, the demand for these muscles increases, making injury prevention and finger strength training essential components of their training regimen.
To prevent injuries, climbers often perform exercises targeting their finger and hand muscles. These exercises include fingerboard workouts, where climbers hang from various holds on a small board, and finger curls, which involve gripping and releasing a small weight. These exercises help increase finger strength, improve grip endurance, and enhance overall climbing performance.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about forearm muscles and the essential gear for climbers, such as Rock Climbing Shoes, it is important to note that the finger and hand muscles are closely connected to the forearm muscles, which provide the necessary power and stability for climbers to exert force and control their movements effectively.
Forearm Muscles
Forearm muscles play a crucial role in climbing, particularly in maintaining grip strength. The repetitive gripping and pulling motions involved in climbing help to develop and strengthen these muscles. Additionally, climbers can benefit from finger extensor training exercises to balance the muscular development in their forearms and prevent muscle imbalances and injuries.
Grip Strength Benefits
Developing grip strength through climbing exercises can lead to significant benefits in forearm muscles. Climbers rely heavily on their grip strength to navigate vertical surfaces, which in turn strengthens their finger flexor muscles and improves forearm endurance. The following are three key benefits of grip strength training for climbers:
- Increased finger flexor strength: Climbing requires a strong grip to hold onto rock surfaces, and this constant gripping motion strengthens the finger flexor muscles, such as the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum superficialis.
- Improved forearm endurance: As climbers progress, they gradually increase the time they spend gripping holds, which helps build endurance in the forearm muscles, allowing them to sustain longer climbs without fatigue.
- Enhanced overall climbing performance: Developing grip strength not only improves forearm muscles but also contributes to better overall climbing performance, as a strong grip is essential for stability and control on the wall.
With a solid understanding of grip strength benefits, let’s now explore the importance of finger extensor training for climbers.
Finger Extensor Training
To effectively train the finger extensor muscles, climbers can incorporate exercises that target this specific area of the forearm. Finger extensor training is essential for injury prevention and finger tendon conditioning in climbers. These muscles, located on the back of the forearm, play a crucial role in maintaining proper balance and stability during climbing movements. One effective exercise is finger extensions, where climbers use a rubber band or finger extensor bands to resist the extension of the fingers.
Another exercise is finger rolls, where climbers roll a weighted bar up and down using only their fingers. By regularly incorporating these exercises into their training routine, climbers can strengthen their finger extensor muscles, improving their grip strength and reducing the risk of finger injuries. Moving on to the next topic, let’s now explore the importance of core muscles in climbing.
Core Muscles
The core muscles play a crucial role in climbing, providing stability, balance, and power. These muscles are engaged throughout the climbing movement, from maintaining body position to generating force for upward movement. Some of the key muscles involved in climbing include the rectus abdominis, obliques, erector spine, and hip flexors. To strengthen the core for climbing, exercises such as planks, hanging leg raises, and Russian twists can be incorporated into training routines.
Importance of Core
Climbers frequently rely on their core muscles for stability and balance during their ascent, highlighting the vital role of these muscles in their performance. The core muscles, which include the abdominals, obliques, and lower back, provide a strong foundation for climbers to maintain proper body alignment and control their movements.
The importance of flexibility: The core muscles need to be flexible to allow climbers to move efficiently and maintain balance on the wall. A flexible core helps climbers navigate through various positions and reach for holds in different directions.
The role of balance: Core strength plays a crucial role in maintaining balance while climbing. A strong core helps climbers stabilize their body and distribute their weight evenly, allowing them to make precise movements and maintain control on challenging terrain.
Muscles Involved in Climbing
Core strength is crucial for climbers as it directly impacts their stability, balance, and overall performance on the wall. In addition to the core, climbers engage various muscles in their upper and lower body to successfully navigate challenging routes. The table below showcases some key muscles involved in climbing and their respective functions:
| Muscles | Functions |
|---|---|
| Finger Flexors | Provide finger strength and grip |
| Forearm Flexors | Aid in forearm endurance and grip |
| Biceps | Assist in pulling movements and maintaining arm position |
| Triceps | Aid in pushing movements and stabilizing the arms |
| Latissimus Dorsi | Help with pulling and hanging |
| Glutes | Provide stability and power in lower body movements |
| Quadriceps | Assist in leg extension and stability |
| Hamstrings | Aid in hip extension and leg stability |
| Core Muscles | Contribute to overall stability, balance, and coordination |
Core Exercises for Climbers
To effectively target and strengthen the core muscles, climbers can incorporate specific exercises that enhance their stability, balance, and coordination. Here are three key exercises that climbers can include in their core workout routine:
- Planks: This exercise helps to strengthen the entire core, including the abdominal muscles, lower back, and obliques. It improves stability and endurance, which are essential for climbing.
- Russian twists: By engaging the obliques, Russian twists help climbers develop rotational strength and stability. This exercise also improves flexibility and enhances balance.
- Leg raises: Leg raises target the lower abdominal muscles, hip flexors, and lower back. Strengthening these muscles is crucial for maintaining a stable core while climbing.
Incorporating these core exercises into a regular training regimen can significantly improve a climber’s overall performance. Now, let’s move on to discussing the importance of back and shoulder muscles in climbing.
Back and Shoulder Muscles
One of the primary muscle groups targeted by climbers is the back and shoulder muscles. These muscles play a crucial role in providing stability, strength, and control during climbing movements. Developing back and shoulder flexibility is essential for climbers to execute various climbing techniques effectively and efficiently while reducing the risk of injuries. To improve flexibility and prevent injuries, climbers can incorporate specific exercises and techniques into their training routine.
These may include stretching exercises targeting the back and shoulder muscles, such as cat-cow stretches, shoulder rolls, and thoracic spine mobilizations. Additionally, climbers can benefit from injury prevention techniques such as proper warm-up and cool-down routines, gradual progression in training intensity, and incorporating rest and recovery days into their schedule. By focusing on the back and shoulder muscles and incorporating these injury-prevention techniques, climbers can enhance their performance and minimize the risk of injury.
| Back Muscles | Shoulder Muscles |
|---|---|
| Latissimus Dorsi | Deltoids |
| Trapezius | Rotator Cuff Muscles |
| Rhomboids | Teres Major |
| Erector Spinae | Infraspinatus |
| Multifidus | Supraspinatus |
Leg Muscles
The leg muscles play a crucial role in providing stability and power for climbers during their ascent. Strong and flexible leg muscles are essential for maintaining balance and stability on the climbing wall or rock face. Here are three key leg muscles that climbers work:
- Quadriceps: The quadriceps are located in the front of the thigh and are responsible for extending the knee. They provide the power needed to push off and propel the body upward during climbing.
- Hamstrings: The hamstrings, located on the back of the thigh, help to flex the knee and extend the hip. They are particularly important for maintaining balance and stability while climbing.
- Calves: The calf muscles, including the gastrocnemius and soleus, are located in the lower leg. They play a crucial role in providing power for footwork and maintaining balance on small footholds.
Cardiovascular System Muscles
Climbers engage the muscles of their cardiovascular system to enhance endurance and support sustained climbing performance. The cardiovascular system, which includes the heart, blood vessels, and lungs, plays a crucial role in supplying oxygen-rich blood to the working muscles during climbing. As climbers ascend, their heart rate increases to meet the demand for oxygenated blood. This sustained elevation in heart rate strengthens the heart muscle and improves cardiovascular endurance.
Regular climbing workouts also contribute to improved aerobic fitness. Aerobic exercise, such as climbing, involves continuous, rhythmic movements that increase the heart rate and breathing rate. This type of exercise helps to improve the efficiency of the cardiovascular system, allowing climbers to sustain higher levels of effort for longer periods of time. By engaging their cardiovascular system muscles, climbers can enhance their endurance and overall climbing performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Injuries Climbers May Experience in Their Finger and Hand Muscles?
Climbers commonly experience finger and hand muscle strains and sprains due to the intense physical demands of the sport. These injuries can result from overuse, improper technique, or insufficient warm-up and stretching. Proper training, rest, and rehabilitation are key to preventing and recovering from such injuries.
Are There Any Specific Exercises or Training Techniques to Strengthen Forearm Muscles for Climbing?
To strengthen forearm muscles for climbing, there are various exercises and training techniques available. These include fingerboard exercises, wrist curls, and forearm pronation/supination exercises. Consistent practice and gradual progression are key to building strength and preventing injury.
How Does Core Strength Impact Climbing Performance and What Exercises Can Help Improve It?
Core strength is crucial for climbing performance. It provides stability, balance, and power during moves. Effective core exercises for climbers include planks, Russian twists, and hanging leg raises. Regular training can enhance climbing ability and reduce the risk of injury.
Can Climbing Help Improve Posture and Alleviate Back and Shoulder Muscle Tension?
Climbing can improve posture and alleviate back and shoulder muscle tension by promoting flexibility and preventing muscle imbalances. Through the use of various climbing techniques, climbers engage multiple muscle groups, leading to enhanced overall body strength and alignment.
Are There Any Specific Leg Muscle Groups That Climbers Should Focus on Strengthening?
When it comes to climbing, focusing on leg muscle groups and incorporating leg strengthening exercises is crucial for improving climbing performance. These exercises help activate and strengthen the leg muscles, enhancing overall climbing ability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, climbers engage a wide range of muscles throughout their bodies. From their finger and hand muscles, which provide the essential grip strength, to their forearm muscles, which aid in maintaining control and stability, climbers work various muscle groups. Additionally, their core muscles play a crucial role in maintaining balance, while back and shoulder muscles provide the necessary strength for pulling and pushing movements. Leg muscles are also engaged for stability and propulsion. Lastly, climbing also benefits the cardiovascular system, as it requires sustained effort and promotes endurance.